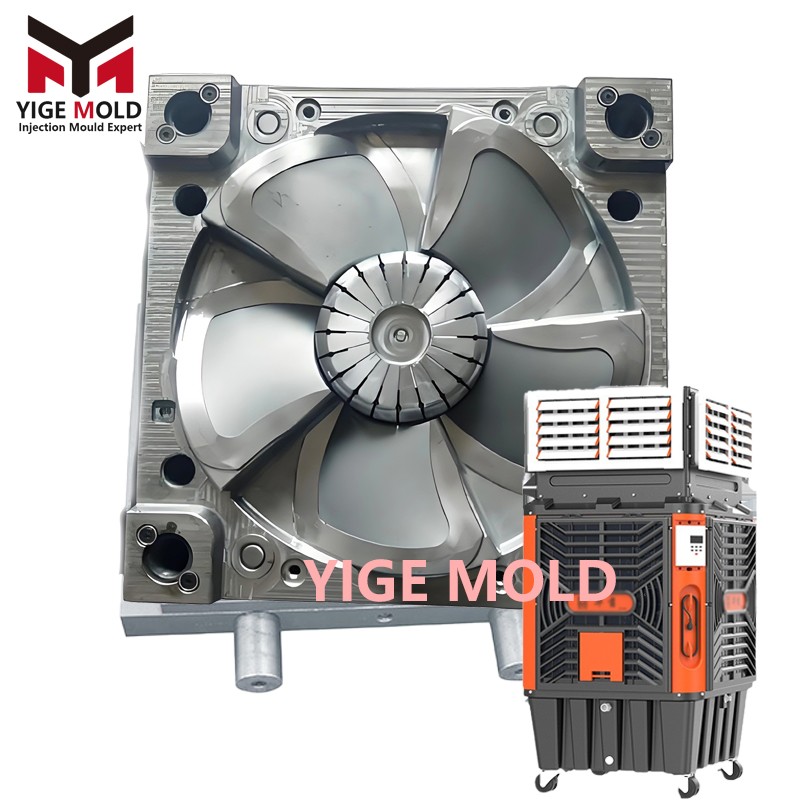
Airflow Housing Mold
Airflow Housing Mold: Engineered for Aero-Structural Precision
Airflow housing molds are specialized high-performance tooling systems designed for manufacturing the aerodynamic enclosures critical to ventilation, thermal management, and air-handling equipment. Unlike conventional housing molds, these tools are engineered to form complex internal geometries that directly influence laminar flow efficiency, turbulence control, and acoustic performance, making aerodynamic fidelity as critical as dimensional accuracy.
The core innovation lies in the bio-inspired parametric design of mold cores and cavities. Internal flow channels are shaped using algorithms derived from natural aerodynamic forms—such as avian wing profiles and respiratory tract geometries—optimized through computational fluid dynamics to minimize pressure loss. The tooling integrates variable-angle diffuser systems within the mold structure itself, allowing for the formation of tapered, helical, or convergent-divergent air passages in a single injection cycle without secondary assembly.
To achieve the necessary surface quality for smooth airflow, these molds utilize micro-milled surface textures (5–30 micron range) and asymmetric cooling circuits that prevent flow-disrupting sink marks on critical internal surfaces. For complex multi-directional air inlets/outlets, a hydraulically synchronized slider matrix operates with micron-level timing precision, creating interlocking features that traditional slides cannot form.
Fiber-reinforced engineering polymers with 30–50% glass or carbon fiber content are standard, requiring hardened tool steels with erosion-resistant coatings to withstand abrasive flow. Mold designs incorporate embedded piezoelectric sensors that monitor flow-induced harmonic vibrations during testing, allowing for mold surface adjustments that shift resonant frequencies and reduce operational noise by 6–8 dB.
The manufacturing process employs non-contact 3D scanning verification of internal passages, ensuring aerodynamic tolerances within ±0.04 mm. This precision enables housing systems to achieve 12–18% improvement in volumetric flow efficiency and a 20–25% reduction in system noise compared to conventionally molded housings, making the mold not merely a shaping tool, but an active contributor to the electromechanical performance of the final product.