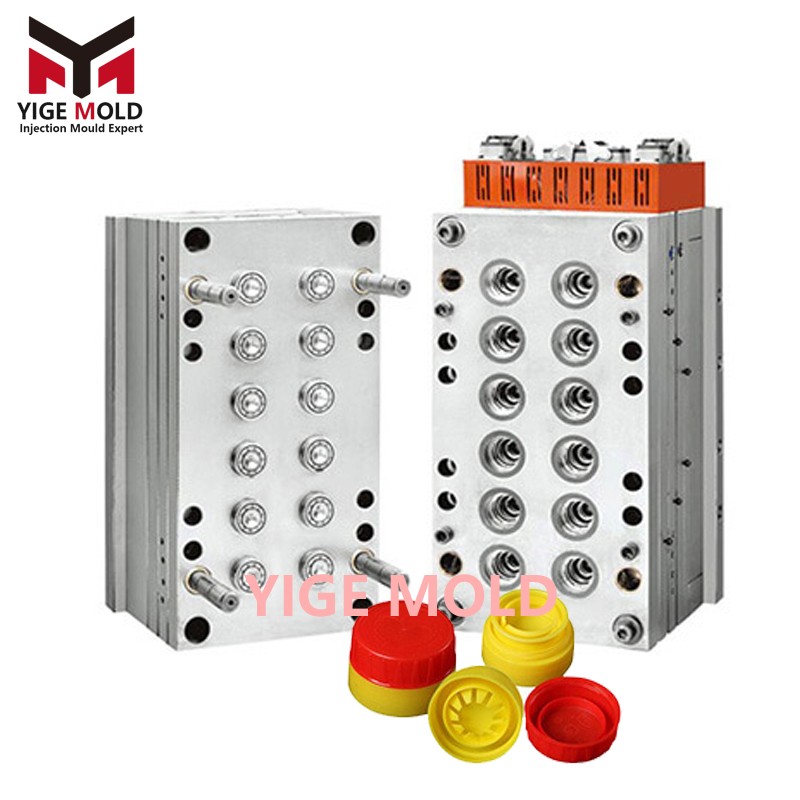
Snap Closure Mould
 Snap Closure Molds: The Art and Science of Precision in Open-Close Mechanisms
Snap Closure Molds: The Art and Science of Precision in Open-Close Mechanisms
Snap closures, a category of packaging seals that utilize an intuitive pressing action for opening and closing, are widely used in daily chemicals, pharmaceuticals, food, and industrial sectors. Their core function—achieving rapid switching between sealing and opening states via vertical pressure that drives the deformation, latching, or displacement of internal mechanisms—places far higher demands on precision and complexity in mold design and manufacturing compared to standard threaded closures. Snap closure molds are the critical process equipment that realizes these complex functions and ensures each pressing action is stable and reliable, representing the pinnacle of precision injection molding.
I. Systemic Complexity: Multi-Dimensional Integration Driven by Function
The essence of a snap closure mold is a dynamic functional system integrating mechanical principles, material properties, and precise mechanical structures. It must achieve the precision molding of multiple components with differing functions and relative motion relationships within a single injection cycle. Its complexity manifests on three levels:
-
Structural Complexity: A typical snap closure (e.g., a common flip-top or pump-action closure) usually comprises multiple components: cap body, hinge, snap features, sealing ribs, spout/drip tube. The mold must form these components, especially the moving joints (like hinges), integrated with the main body in one shot. This requires intricate cavity partitioning and material flow control within the mold.
-
Motion Synergy: The mold must not only form static structures but also create the space and geometry for post-molding "dynamic function." The living hinge is a prime example and a core technical challenge. The mold must form an extremely thin (typically 0.2-0.4mm), precisely dimensioned film-like connecting section at the hinge, capable of withstanding hundreds of thousands of flex cycles. This demands exceptionally precise control over cooling rate and molecular orientation in the hinge area, making cooling channel design and venting in that mold section critical.
-
Stringent Tolerances: The "feel" and seal integrity of a snap closure depend entirely on micron-level fit tolerances between components. The interference fit of snap features (typically 0.05-0.15mm), flatness of sealing surfaces, and clearance between guide posts and holes must all be guaranteed by the machining accuracy of the mold components. Any minor deviation can lead to poor sealing, excessive or insufficient opening force, or even mechanical failure.
II. Deconstruction of Core Technologies: Precision Mechanisms Enabling Dynamic Function
The design ingenuity of snap closure molds lies in specialized mechanisms that ensure successful molding and ejection of complex structures:
-
Complex Ejection and Side-Action Systems:
-
Undercut Release for Internal Snaps: Internal snap features often require lifters or internal side-action slides. These mechanisms move at specific angles during mold opening, first releasing the undercut space of the snap before participating in the overall ejection.
-
Handling External Undercuts: For decorative or grip features on the outer wall that create undercuts, external slides are designed.
-
Sequential Ejection Mechanisms: For particularly complex closures, different mold sections may need to separate in a strict sequence, requiring hydraulically or mechanically actuated sequential mold opening controls.
-
-
Miniaturization and High-Precision Molding Systems:
-
Micro-Runner and Gate Technology: Many parts of snap closures (e.g., hinges, small snaps) are minute, requiring precise melt filling without excessive shear stress. Pin-point hot tips or fan gates are used, with precise control over injection speed and pressure profiles.
-
Inserts and Conformal Cooling: Extensive use of micro-inserts made from high thermal conductivity materials (like beryllium copper) in critical areas like hinges and snaps, equipped with dedicated conformal cooling channels. This enables rapid, targeted cooling to optimize crystalline structure and internal stress, key to hinge longevity.
-
-
Flash Prevention and Precision Venting Design:
The multiple mating surfaces for moving parts are potential flash points. Flash immediately impairs the closure's function. The mold must maintain extremely high fit accuracy (often requiring hand fitting) on all moving component interfaces (slides, lifters). Simultaneously, precision venting channels with depths of only 0.01-0.02mm are designed at the end of flow paths in thin-walled areas like hinges to ensure air escape, preventing short shots or burns from trapped air.
III. Differentiated Design Philosophy Across Applications
The core design focus of snap closure molds varies drastically depending on the end-use:
-
Daily Chemical Closures (e.g., shampoo flip-tops, facial wash snap caps):
-
Design Core: Tactile feel and aesthetic quality. Pursuit of a crisp "click" sound and comfortable opening/closing force. Mold surfaces require high-gloss polish or fine texturing for premium appearance. Extreme demands on hinge durability (often requiring tens of thousands of cycle tests).
-
Material Consideration: Often use PP, PE for good flexibility. Mold design must account for their higher shrinkage.
-
-
Pharmaceutical & Food Packaging Closures (e.g., child-resistant locks, press-to-open pour spouts):
-
Design Core: Safety and sealing integrity. E.g., child-resistant closures requiring a specific dual-action (push & turn) to open involve extremely complex internal interlocking mechanisms. Sealing must prevent leakage, demanding high precision on sealing surfaces and excellent mold cleanability.
-
Material Consideration: May use PP, PET, requiring hygienic grades. Mold steel and runners must be easy to clean without dead spots.
-
-
High-End Functional Closures (e.g., vacuum pumps, dispensing closures):
-
Design Core: Complex internal functional structures and airtightness. These closures often contain pistons, spring chambers, check valves, etc., frequently requiring multi-material molding (hard/soft) or post-mold assembly. The "mold" may be a system of multiple sub-molds enabling in-mold assembly (IMA).
-
Pinnacle of Technology: Represents the highest complexity in snap closure molds, involving precision fits, elastomeric seals, and multi-part dynamic interactions.
-
IV. Manufacturing Challenges and Quality Assurance Systems
-
Manufacturing Challenges:
-
High-Precision Machining: Manufacturing and assembling numerous miniature slides, lifters, etc., with tight tolerance control is the core challenge.
-
Longevity Requirements: Moving parts undergo frequent friction and impact, demanding high wear resistance. Use of powder metallurgy high-speed steels with PVD coatings (e.g., TiN, TiAlN) is common.
-
Mold Tryout and Debugging: Lengthy debugging cycles involving repeated tests for opening force, seal integrity, hinge fatigue—an iterative process of "design-build-test-optimize."
-
-
Quality Assurance:
-
Upfront Process Simulation (CAE): Essential use of mold flow analysis software during design to simulate filling, cooling, warpage, fiber orientation (if using reinforced materials), predicting and resolving potential issues like weld lines or stress concentration in hinge areas.
-
Systematic Testing: Beyond dimensional checks, dedicated opening force testers, leak testers, hinge fatigue testers are used for quantitative functional validation.
-
Snap closure molds can rightfully be called the "crown jewel" of the plastic mold industry. They transform cold steel and precise mechanisms into the smooth, reliable, and comfortable pressing experience at the user's fingertip. Their development level collectively reflects a nation's comprehensive capability in precision mold design, advanced material application, micro-fabrication, and system integration. From the simple cap of a lipstick tube to the complex pump of a functional skincare product, every convenient opening is underpinned by the profound engineering intelligence and relentless technical pursuit embodied in snap closure molds. On the evolving path toward more user-friendly and functional packaging, innovation in snap closure molds will continue to play an indispensable and pivotal role.