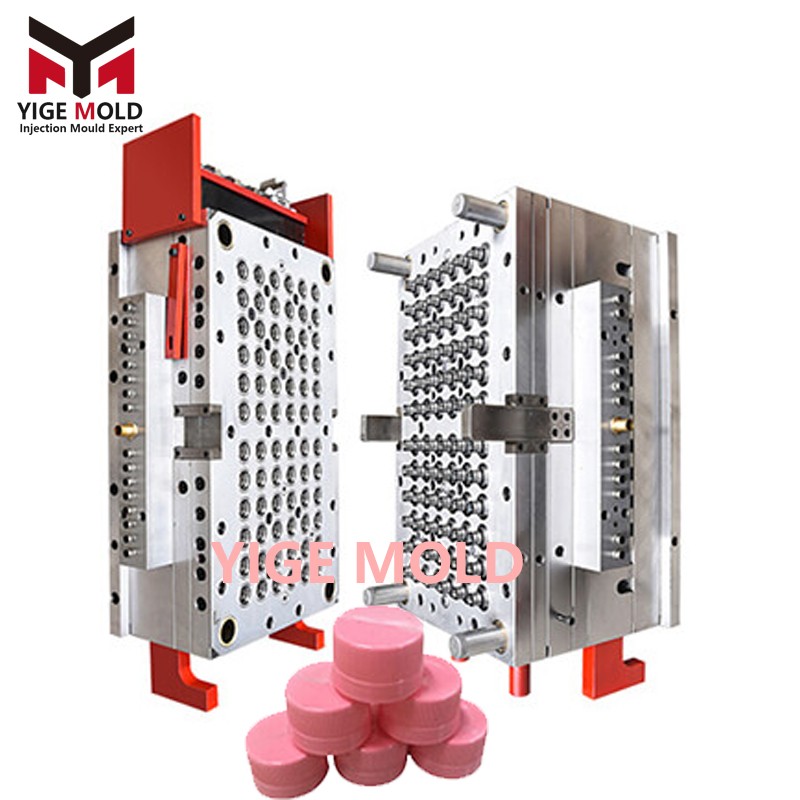
Threaded Cap Mould
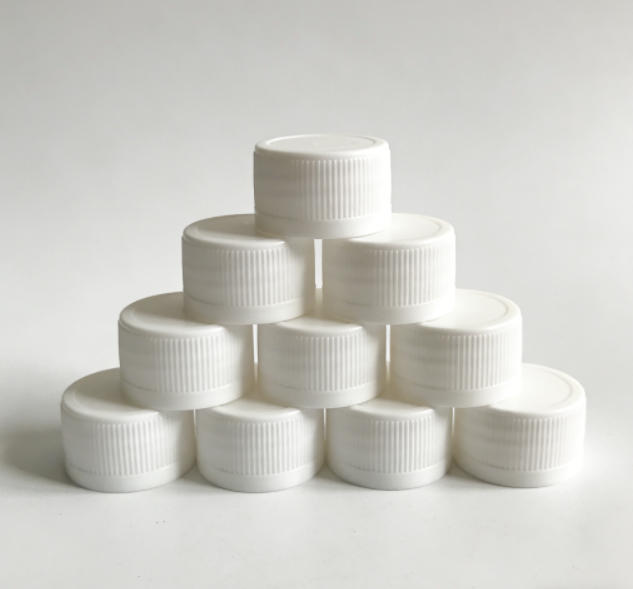 Threaded Cap Mould: Core Process Equipment in Precision Manufacturing
Threaded Cap Mould: Core Process Equipment in Precision Manufacturing
Threaded cap moulds serve as essential foundational equipment in the modern packaging industry, undertaking the mass production tasks for various types of threaded closures, including beverage bottle caps, pharmaceutical container caps, and packaging caps for daily chemical products. The design and manufacturing level of this specialised tool directly impact the sealing performance, user experience, and production efficiency of packaged products, making it an important indicator for measuring a country's technological prowess in injection moulding.
I. Technical System and Structural Composition
The technical system of threaded cap moulds is built upon the foundation of precision mechanical design and materials engineering, primarily consisting of five major functional systems:
The Moulding System forms the core functional unit of the mould, composed of cavities and cores that create a precisely matched moulding space. This system determines the geometric parameters of the threads, the form of the sealing structure, and the appearance characteristics of the product. Mould materials are typically high-quality tool steels such as S136 and NAK80, which after precision heat treatment achieve a hardness of HRC 48-52, ensuring dimensional stability during long-term production.
The Thread Release System represents a key technical challenge, employing various mechanical structures to facilitate the smooth ejection of complex threads. A rotating ejection mechanism drives the core rotation via gears and racks or a hydraulic motor, allowing the part to unscrew naturally along the thread path. Slide core-pulling structures are suitable for interrupted threads or special tooth profiles. Collapsing mechanisms achieve deep thread release through the specific angular movement of angle pins.
The Runner System adopts a fully hot runner technical solution, comprising a manifold, heating elements, and hot nozzles to form a complete hot runner system. Multi-cavity moulds are equipped with valve gate sequential control systems, capable of precisely managing the fill timing for each cavity. This ensures consistent fill results across dozens or even hundreds of cavities, keeping product weight variation within ±0.02 grams.
The Temperature Control System achieves efficient heat exchange through a meticulously designed network of cooling channels. The layout of cooling channels is optimised based on mould flow analysis results, utilising conformal channel designs to ensure uniform cooling. For critical areas such as thread roots, specialised inserts made from high thermal conductivity materials like beryllium copper are often used to achieve localised enhanced cooling.
The Ejection and Guidance System consists of precision motion mechanisms including ejector pins, return pins, and leader pins with bushings. The ejection system layout is calculated based on mechanical principles to ensure even force distribution on the part. The guidance system employs high-precision leader pins matched with oil-free bushings, guaranteeing precise alignment is maintained during high-speed operation.
II. Manufacturing Processes and Technical Requirements
The manufacturing process of threaded cap moulds reflects the highest level of modern precision machining technology. The machining accuracy required for cores and cavities is within 0.005 millimetres, with thread electrode fabrication precision controlled at the 0.002-millimetre level. The manufacturing process comprehensively utilises technologies such as high-speed milling, precision EDM, and slow wire EDM. Critical fitting surfaces require hand fitting to ensure mating precision.
Mould service life is a key technical indicator. Through the use of high-quality tool steels, appropriate heat treatment processes, and surface enhancement technologies, the service life of modern threaded cap moulds generally exceeds 10 million cycles. For high-speed production beverage cap moulds, a service life exceeding 20 million cycles is often required.
High cavitation is a primary development direction, with cavity counts evolving from 32, 64 to 128, 144, and even higher. The design of multi-cavity moulds must address technical challenges such as runner balancing, uniform cooling, and structural rigidity to ensure each cavity can stably produce qualified parts.
III. Professional Requirements Across Application Fields
The Beverage Packaging Sector places the highest demands on production efficiency, with mould design primarily characterised by high-speed and multi-cavity configurations. Typical applications include mineral water bottle caps and carbonated beverage bottle caps. Mould design focuses on the moulding precision of tamper-evident bands and the stability of opening force, with production cycles typically controlled between 3-5 seconds.
The Food and Pharmaceutical Packaging Sector emphasises safety and hygiene performance. Mould materials and structures must comply with hygiene standard requirements. Child-resistant closure moulds need to realise complex interlocking mechanisms to ensure opening is only possible through specific actions. Pharmaceutical cap moulds require dead-zone-free designs to facilitate thorough cleaning and disinfection.
The Daily Chemical Products Sector prioritises appearance and user experience, demanding higher surface treatment technology for moulds. Cosmetic cap moulds need to achieve mirror polishing or special texture effects. Some high-end products require complex processes like two-shot moulding or insert moulding.
The Industrial Packaging Sector involves larger product sizes, placing higher demands on mould strength and rigidity. Chemical drum cap moulds need to withstand higher injection pressures to ensure complete moulding of thick-walled products. Special-purpose packaging caps need to meet specific performance requirements such as chemical resistance.
IV. Technological Development Trends
The pursuit of high efficiency continues to drive technological progress. By optimising runner design and cooling systems, production cycles are continuously shortened. The application of stack mould technology doubles the output per unit clamping force while reducing energy consumption by over 30%. New hot runner systems utilise zoned temperature control, further enhancing production stability.
Functional integration has become a key development focus, with a growing trend toward a single mould realising multiple functions. Integrated designs for features like tamper-evident bands, anti-counterfeiting structures, and QR code platforms reduce subsequent processing steps. One-shot moulding technology for inner seal structures improves the product's sealing reliability.
Increasing demands for new material adaptability require mould designs to account for the characteristic differences of various materials. Processing biodegradable materials requires special temperature control and venting design. The use of recycled materials demands moulds with better wear resistance and a wider processing window.
Specialisation and division of labour are becoming more refined, with increasingly close technical cooperation between mould manufacturers, material suppliers, and injection moulding machine manufacturers. The development of specialised moulds for specific products requires collaborative innovation across all segments of the industrial chain, forming a complete technical service system.
V. Quality Control System
Mould manufacturing establishes a comprehensive quality control process with strict standards from design review and machining processes to final acceptance. The design phase utilises mould flow analysis to predict potential defects and formulate corresponding preventive measures. The machining process employs online inspection technology to ensure the machining accuracy of each component. After assembly, comprehensive functional testing is conducted, including checks for clamping accuracy, ejection smoothness, and thread fit.
The product validation phase simulates actual production conditions, conducting continuous production tests to verify mould stability and product qualification rates. For high-speed multi-cavity moulds, statistical analysis of weight and dimensions for parts from each cavity is also required to ensure consistency in mass production.
VI. Industry Value and Prospects
Threaded cap moulds hold an irreplaceably important position in the modern packaging industry chain. Their technological level directly influences the development of the entire packaging sector. With the continuous growth of global packaging demand and the trend of consumption upgrading, the demand for high-end threaded cap moulds will maintain steady growth.
Technological development will continue to advance in the direction of efficiency, precision, and specialisation. The application of new materials and processes will drive continuous upgrades in mould technology. As a significant global manufacturing base for moulds, the United Kingdom has established a complete technical system and industrial support in the field of threaded cap moulds and is progressing toward higher technological levels.
Technological advancements in mould manufacturing not only enhance the quality of packaging products but also drive technological upgrades in related industries. From raw material preparation to injection moulding, and from product design to quality control, the development of threaded cap mould technology stimulates technological innovation across the entire industrial chain.
Looking ahead, threaded cap moulds will continue to achieve breakthroughs in precision, efficiency, and reliability. They will provide higher quality technical equipment support for the global packaging industry, meeting the growing demand for packaging while steering the sector towards higher quality and more sustainable development.