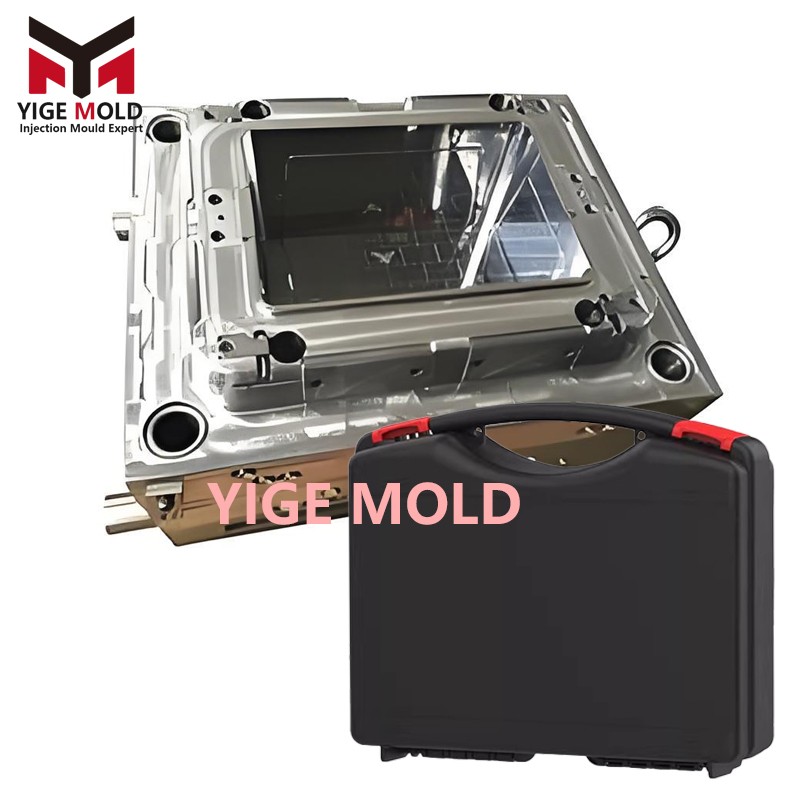
Plastic tool box mold
 Plastic Toolbox Mold: The Precision Manufacturing Core of Professional Storage Solutions
Plastic Toolbox Mold: The Precision Manufacturing Core of Professional Storage Solutions
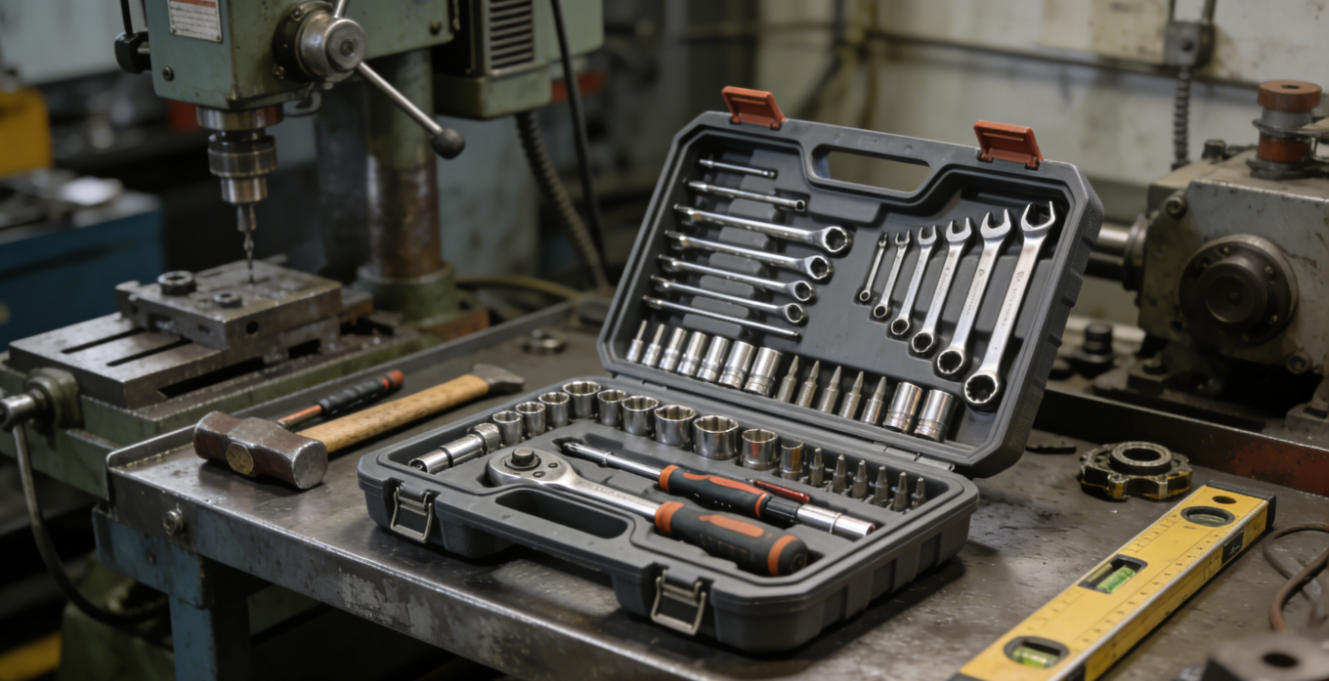
Plastic toolboxes are indispensable equipment in modern industry, maintenance, and household tasks. The manufacturing level of their molds directly determines the product's durability, functionality, and user experience. An excellent plastic toolbox mold is not merely a production tool but a precision engineering system that integrates ergonomics, materials science, and structural mechanics.
I. Core Product Functions and Mold Design Challenges
The design of a plastic toolbox mold must fundamentally serve the core usage requirements of the product, presenting multiple technical challenges:
-
Balancing Structural Strength and Lightweight Design
-
Challenge: Toolboxes must withstand heavy tool loads (often 20-30 kg) and potential drop impacts while remaining easy to carry, demanding lightweight construction.
-
Mold Solution:
-
Scientific Rib Design: Utilizing mold flow analysis and structural simulation to design a three-dimensional, crisscrossing network of reinforcing ribs inside the box body. Rib thickness is optimized to 50%-60% of the main wall thickness, with optimized height and spacing to achieve maximum rigidity with minimal material use.
-
Reinforcement at Key Areas: The mold incorporates designs for localized wall thickening or high-strength inserts at stress concentration points like the four corners of the box, handle mounting points, and latch areas. This ensures these areas are densely packed during injection molding, free from sink marks.
-
-
-
Complex Opening/Closing and Latching Systems
-
Challenge: Toolbox hinges must endure tens of thousands of open/close cycles, and latches must ensure a tight seal while being easy to operate.
-
Mold Solution:
-
Multi-Axis Hinge Formation: Employs complex mechanisms involving multiple sliders and lifters working in coordination to form multi-segment hinges (internal or external) in a single shot, ensuring smooth rotation and long service life.
-
Precision Latch System: The undercut angle of the latch hook and the thickness of the flexible wall require precision in the mold to within 0.02mm. Mechanisms like delayed core pulling or internal sliders are typically used to form complex internal undercuts, guaranteeing a secure "click" feedback and firm closure.
-
-
-
Modular and Multi-Functional Interior
-
Challenge: Modern toolboxes feature movable partitions, tool holders, small parts drawers, and other modules.
-
Mold Solution: This often requires coordinated sets of molds. The main box mold forms the guide rails and locating posts. The movable components (partitions, drawers) require separate high-precision small molds with even stricter dimensional tolerances to ensure perfect fit and smooth sliding with the main body.
-
II. Precision Engineering in Mold Manufacturing
-
High Wear Resistance and Long-Life Structure
Toolbox molds must withstand several hundred thousand to over a million cycles of high-pressure injection. Critical components are made from pre-hardened quality mold steels (e.g., P20, 718) or hardened steels (e.g., H13). At high-wear areas like hinge pins and latches, wear-resistant inserts (e.g., imported S136) are used with titanium-based or Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC) coatings, extending service life by 2-3 times.
-
Efficient Cooling and Venting Systems
-
Conformal Cooling Technology: For deep cavities and thick-walled sections like handles, 3D-printed conformal cooling channels or beryllium copper inserts are employed, increasing cooling efficiency by over 30%. This significantly shortens cycle times and reduces warpage.
-
Multi-Stage Venting Design: At areas where melt flow ends, such as rib terminals and deep within cores, porous venting steel inserts and micro-vents (0.015-0.02mm deep) are placed. Main venting channels are also incorporated on the parting line to completely avoid short shots or burn marks caused by trapped air.
-
-
Perfect Surface Finish and Texture
-
Anti-Slip and Scratch-Resistant Texture: The exterior surface typically features a fine leather or grid texture achieved through chemical etching or laser engraving of the mold. The texture design must balance anti-slip feel, scratch concealment, and ease of demolding.
-
High Gloss and Logos: Brand logos, measurement markings, etc., are formed by mirror-polished or laser-engraved surfaces on the mold, ensuring clarity and permanence.
-
III. Special Processes and Innovative Applications
-
Two-Color / Soft Overmolding
To enhance grip comfort and anti-slip properties, handles or box edges often combine a rigid PP/ABS body with a soft TPE/TPR overmold. This requires two-shot injection molds or secondary overmolding molds, demanding extremely high precision (typically within ±0.03mm) and material compatibility.
-
Gas-Assisted Injection Molding (GAIM) Application
For very large toolboxes or those with thick sections (like reinforcement beams), GAIM can be used. The mold must be designed with special gas injection pins and channels to inject high-pressure nitrogen during molding, creating a hollow structure. This can reduce weight by 15%-30% while maintaining strength and eliminating sink marks.
-
In-Mold Assembly (IMA) Technology
The most advanced technique involves pre-placing inserts like hinge pins or metal latches into the mold, completing assembly during the injection process. This requires the mold to have a precision insert positioning and feeding system, dramatically reducing post-molding assembly steps and improving production efficiency and consistency.
IV. Quality Control and Testing Standards
A qualified mold must pass rigorous verification:
-
Dimensional Accuracy Verification: Using a Coordinate Measuring Machine (CMM) to fully inspect box dimensions (length, width, height, diagonals) and wall thickness, ensuring compliance with design tolerances (typically within ±0.15mm).
-
Assembly and Functional Testing: Simulating real-world use with tens of thousands of open/close cycle tests, load-bearing drop tests, and latch fatigue tests.
-
Mass Production Stability Validation: Conducting pilot runs of 5,000-10,000 continuous cycles, monitoring Key Process Capability Indices (CPK ≥1.33) for product weight and critical dimensions to ensure mold stability and reliability.
V. Market Trends and Value Creation
-
Lightweighting and Sustainability: Mold design is evolving towards thinner walls and optimized structures to reduce plastic consumption. Simultaneously, molds must accommodate the processing characteristics of recycled plastics.
-
Customization and Smart Features: Modular mold design enables interchangeable panels, allowing for customer customization of colors and surface graphics. In the future, molds may integrate sensors for production monitoring.
-
Value Creation for Clients: A high-quality toolbox mold is the foundation for a manufacturer's product moat. It directly delivers:
-
Product Competitiveness: Superior functionality, durable quality, and excellent user experience.
-
Production Cost Advantages: High production efficiency, low scrap rates, and long mold life.
-
Market Responsiveness: Modular design allows rapid derivation of new styles, capturing market opportunities.
-
Conclusion
A plastic toolbox mold is far more than a simple container-forming tool. It is the engineering bridge that transforms user expectations for sturdiness, lightness, and convenience into a tangible product. From scientific rib design to complex kinematic mechanisms, from durable material selection to innovative molding processes, every detail embodies a profound understanding of function and manufacturability. Investing in a well-designed, precision-manufactured toolbox mold is an investment in the future market success of the product and the solid foundation of the brand's reputation. In the professional tool sector, a reliable toolbox itself embodies craftsmanship, and the mold that creates it represents the ultimate expression of this spirit at the level of industrial manufacturing.